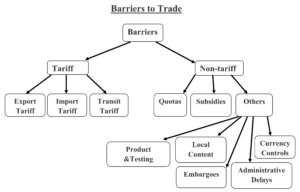
Barriers to Trade
The barriers generally include tariff and non-tariff strategies.
1. Tariffs
A tariff is a tax imposed on goods involved in international trade.Tariffs are imposed on goods imported,in which case they are called import duties.Taxes are also imposed on goods when they leave the country(export tariff) or as they pass through one country bound for another(transit tariff).
Tariffs may be either ad valorem or specific.Ad valorem tariffs are imposed as percentages on values of goods imported.Specific tariffs relate to some specific attributes of the goods-weight,quantity,and value.A compound tariff is also levied and is calculated partly as a percentage on value and partly as a rate per unit or weight.
2. Non-Tariffs
A second category of government interventions on international trade related to non-tariff barriers.Any government regulation,policy or procedure other than a tariff that has the effect of restricting international trade,or affecting overseas investment,become a non- tariff barrier.Following can be considered in this context:
a) Quotas
Quotas refer to numerical limits on the quantity of goods that may be imported into a country during a specific period.The quantity of goods that may be imported is stated in license issued to a group of individuals or firms.The importer has to pay a penalty if the quantity imported exceeds the one specified in the license.Most countries use quotas to protect politically powerful or vulnerable industries,such as agriculture,textiles and motor vehicles,from the threat of foreign competition.With regard to textiles,countries placedquotas on imports under what is called multi-fiberarrangement, which is part of the GATT agreement.
b) Subsidies
A subsidy is a government payment to a domestic producer.Subsidies take several forms including cash grants,low-interest loans,tax breaks,and government equity participation in local firms.By lowering costs,subsidies help domestic producers in two ways:they help them compete against low-cost foreign imports and gain access to export markets.
c) Other Barriers
Countries also use a variety of non-tariff barriers to protect firms from foreign competition.Such barriers include embargoes,local content requirements,administrative delays,currency controls,and product and testing standards.