Cross-Cultural Communication
Meaning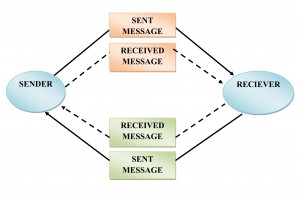
Translating meanings into words and behaviours that is, into symbols—and back again into meanings is based on a person’s cultural background and is not the same for each person. The greater the difference in background between senders and receivers, the greater the difference in meanings attached to particular words and behaviours.
Cross-cultural communication occurs when a person from one culture sends a message to a person from another culture. Cross-cultural miscommunication occurs when the person from the second culture does not receive the sender’s intended message. The greater the differences between the sender’s and the receiver’s cultures, the greater the chance for cross-cultural miscommunication.
Cross-cultural communication has become strategically important to companies due to the growth of global business, technology and the Internet. Understanding cross-cultural communication is important for any company that has a diverse workforce or plans on conducting global business. This type of communication involves an understanding of how people from different cultures speak, communicate and perceive the world around them.
Definition
Lustig and Koester defined it as “the presence of at least two individuals who are culturally different from each other on such important attributes as their value orientations, preferred communication codes, role expectations, and perceived rules of social relationship.”
Frameworks and cultural dimensions most applicable to cross-cultural communication in business:
I. Hofstede‟s cultural dimensions model
II. Hall & Hall‟s cultural value orientations
III. Language: verbal and non-verbal
I. Hofstede’s cultural dimensions
Geert Hofstede is a Dutch social psychologist and anthropologist who has studied the interactions between cultures.The theory is based on the idea that value can be placed upon six cultural dimensions. These are power (equality versus inequality), collectivism (versus individualism), uncertainty avoidance (versus uncertainty tolerance), masculinity (versus femininity), temporal orientation, and indulgence (versus restraint). Hofstede gathered most of his data on world cultural values through surveys conducted by IBM, a US-based technology and consulting firm.
1.Power Distance:
This dimension expresses the degree to which the less powerful members of an organisation accept and expect that power is distributed unequally.It measures the degree to which a culture believes how institutional and organizational power shoul be distributes and whether the decisions of the power holders should be accepted or challenged.
2. Individualism vs. Collectivism:
This dimension focuses on the questions about whether people prefer a close knit network of people or prefer to be left alone to fend for themselves. Hofstede’s Collectivism verses Individualism‘ dimension relates to the degree to which people in a culture prefer to act as members of a group or as individuals. It also reflects whether the group‘s interests are most important or the individual person‘s interest. In organizations in strong individualistic cultures, employees who perform inadequately get dismissed and employees who perform well get bonuses. Collectivistic companies employ not only an individual but also a person; belonging to a group. It is not unusual that the person is a relative of the manager or of one of the employees.
3. Masculinity Vs. Femininity:.
Masculine cultures stress earnings, recognition and challenge whereas feminine cultures stress good working relationship, cooperation and employment security. Masculine and feminine cultures create different management types. In a masculine organization the manager is decisive and makes most decisions single handed. Opposite is 15 true in feminine cultures where this autocrat leadership is frowned upon. In feminine cultures there is a preference for making decisions in a group and the manager is less visible. Masculine and feminine cultures create different management types. In a masculine organization the manager is decisive and makes most decisions single handed. Opposite is 15 true in feminine cultures where this autocrat leadership is frowned upon. In feminine cultures there is a preference for making decisions in a group and the manager is less visible.
4. Uncertainty Avoidance:
This dimension expresses the degree to which the member of the organization feels uncomfortable with uncertainty and ambiguity. In cultures know for high uncertainty avoidance, people feel comfortable in structured and known situations. Employees in weak uncertainty avoidance cultures however do not feel as threatened by unpredictable situations. They accept risks to a greater extent and they adapt easier to changeable situations. Instead employees from weak uncertainty avoidance companies seem to have an emotional fear of formal rules and laws.
5. Long-term vs. Short-term Orientation:
Long-term orientation versus Short-term‖ dimension deals with the time aspect and cultures‘ attitudes towards the past, present and the future. In long-term cultures family companies are common. The working environment has a stable hierarchy which makes it easier for new companies to set up business in the country. This can affect the entrepreneur market negatively, since the people do not stress initiative and risk taking in these cultures. Short-term companies the employees focus on the last month, quarter or last year‘s result. Their control systems are based on this short period and their managers are being judged by the last year‘s results. In long-term companies employees aim for future goals and these are often set 5- 10 years ahead.
6. Indulgence versus Restraint
Indulgence –society that allows relatively free gratification of basic and natural human drives related to enjoying life and having fun.Restraint-society that suppresses gratification of needs and regulates it by means of strict social norms.

