VALUE CHAIN MODEL
A value chain for a product is the chain of actions that are performed by the business to add value in creating and delivering the product. For example, when you buy a product in a store or from the web, the value chain includes the business selecting products to be sold, purchasing the components or tools necessary to build them from a wholesaler or manufacturer, arranging the display, marketing and advertising the product, and delivering the product to the client.
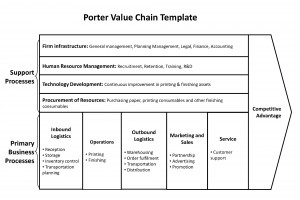
The value chain model, as originally demonstrated by Porter (1985), identifies nine strategically relevant activities that create value and reduce cost in a specific business. These nine value-creating activities consist of five primary activities and four support activities. The primary activities represent the sequence of bringing materials into the business (inbound logistics), converting them into final products (operations), shipping out final products (outbound logistics), marketing, and service. The support activities include procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure. This model is very helpful for identifying specific activities in business where competitive strategies can be applied and where information systems are most likely to have a strategic impact. Successful implementation of e-commerce in an organization should be based on a thorough understanding of the areas in the value chain where e-commerce can add value most. More importantly, to succeed in gaining competitive advantage, e-commerce is to be based on the overall corporate strategy . Among a host of critical areas/ factors in the value chain that major organizations have taken into consideration for establishing a sound e-commerce strategy include role of intermediaries, value pricing, logistics/purchasing, fulfilment, and value nets among others. Following sections present an analysis of these areas.
1. Role of Intermediaries
Intermediaries may be more important now than ever before because most of the rapidly growing Internet businesses are essentially middlemen . For example, companies such as Amazon, CD-Now, Egghead.com, Cisco, and E*Trade can all be thought of as middlemen-resellers of products provided by some other source. Intermediaries will continue to be important because they provide consumers with selection, specialized distribution, and expertise . Some internal disintermediation may take place, in which employees will be removed if they add little value or even negative value to the distribution channel. For example, Dell, Cisco, and some online brokerages have eliminated staff in an attempt to realize cost savings in certain areas. Exhibit 1 illustrates an example of the role of intermediaries in the process of purchasing a book online from Amazon.com.
2. Value Pricing
In addition to employing e-commerce technology to enhance distribution channels, this technology is also used to redefine pricing strategies. Most companies pursuing a premium pricing strategy, for example, can use the Internet to better understand their customers. The Internet allows companies to price with far more precision than they can off-line and to create enormous value in the process. Value pricing involves several approaches. One approach to pricing involves businesses offering heavily discounted prices in an attempt to attract customers to their web sites. Another approach involves businesses transferring their “off-line” prices to the Internet. Neither of these approaches is very efficient because they do not maximize value. An attractive alternative approach is to utilize the Internet to track customers buying habits and adjust prices accordingly, thereby uncovering new market segments. The Internet allows companies to test prices continually in real time and measure customer responses.
3. Brand Differentiation/Loyalty
Pricing is just one of several ways for a company to differentiate itself from the competition. Another way in which a company can differentiate itself is by promoting brand loyalty. Brand loyalty encourages repeat customers and helps to create long-term profitability. A major benefit of customer loyalty is that loyal customers often refer new customers to a supplier.
4. E-Procurement
E-commerce technology has provided organizations with the capabilities to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the logistics and purchasing functions. Firms such as Wal-Mart and Amazon.com are currently outsourcing delivery, relying on logistics companies to deliver the product to the customer. E-procurement is the term currently used to denote the process of using the Internet to integrate supply chain partners through collaboration on key initiatives and to improve the purchasing process within organizations. A major benefit of e-procurement is the cost savings aspect. In fact, organizational costs of placing orders can be reduced by as much as 75% through utilization of the Internet. It also offers organizations the ability to use the Internet to search for the best pricing available. The overall advantage of practising e-procurement is the fact the more automation allows partners quicker access to information. E-procurement also results in better communication among supply chain partners and consequently better supplier-customer relationships. Organizations are able to maintain tighter control over the purchasing process. Only those suppliers that organizations deem to be “preferred suppliers” will be able to transact business with the organization. Currently, e-procurement is being utilized primarily for the purchase of office supplies and items which are used for repair and maintenance of the organization’s facilities (Smock, 2001).
5. E-Fulfilment
Today’s marketplace offers new challenges to organizations. A key initiative organizations have undertaken to better compete is that of “E-fulfilment”. It can alter the way customers purchase as well as the manner in which manufacturers deliver the product to consumers. Technology has also allowed distributors and suppliers to focus on providing value-added services to complement their product offering. E-Fulfilment contrasts with traditional fulfilment. Suppliers are now capable of accepting order online via the Internet and having the information sent directly into their order processing systems, something not possible via traditional fulfilment. Orders placed via e-fulfilment tend to be smaller than those placed via traditional fulfilment channels. The expected and actual lead times are shorter than those witnessed via traditional fulfilment.
6. Value Nets
Firms are continually seeking out new ways to attract and maintain customers. A development that has proven to be effective in attracting and servicing customers is that of the Value Net. A value net is a network consisting of partnerships, which assists in the transfer of information among supply chain partners on a regular basis. The main benefit of a value net is the competitive advantage it offers to all participating organizations. The primary concept behind a value net is its ability to allow firms to address and solve customer problems, rather than just selling a product. A popular trend in the marketplace to address niche markets is that of the online-service company. This form of business interacts directly with the customers primarily via the Internet. The advantage of this form of business is that it provides enhanced service to the customer in the form of direct door-to-door delivery for customers. This is a distinct competitive advantage that firms are looking to exploit
In the world of e commerce companies can use the internet technology to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of particular value chain activities.There are commercially available hardware ad software specifically meant to address management problems associated with the supply and distribution chain or the value chain system as a whole.
Specifically,the Internet technology benefits business organizations in the following ways:
- It is a powerful tool for better supply chain management.
- It is critical to internal operations such as just in time inventory,gear production schedules and production quantities to buyer orders,more accurate monitoring of buyer preferences and shifts in demand and
It is extremely useful for collaborative data sharing with distribution channel partners-online systems reduce transactions costs.