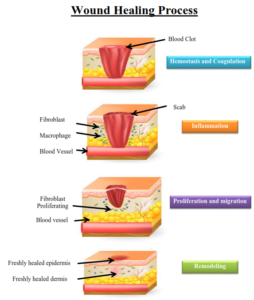
Process of Healing
The healing process is more or less identical in all types of tissue damage, be it inflammatory damage or injuries. The latter situation is covered by the term wound, which simply means damaged tissues generally by physical injury. Healing of wounds is not possible without the participation of inflammatory cells chemical mediators and blood vessels that are also the essential components of an inflammatory process.
The wound healing process is a dynamic one which can be divided into three phases.
- Inflammatory phase
- Proliferation phase
- Maturation phase
- Inflammatory phase
The inflammatory phase is the body’s natural response to injury.During inflammatory phase 2 major processes take place:
- Clotting
Healing of a wound begins with clot formation to stop bleeding and to reduce infection by bacteria, viruses and fungi. Clotting is followed by neutrophil invasion three to 24 hours after the wound has been incurred, with mitoses beginning in epithelial cells after 24 to 48 hours .
- Inflammation
In the inflammatory phase, macrophages and other phagocytic cells kill bacteria, debride damaged tissue and release chemical factors such as growth hormones that encourage fibroblasts, epithelial cells and endothelial cells which make new capillaries to migrate to the area and divide.
2. Proliferation phase
During proliferation, the wound is ‘rebuilt’ with new granulation tissue which is comprised of collagen and extracellular matrix and into which a new network of blood vessels develop, a process known as ‘angiogenesis’. Healthy granulation tissue is dependent upon the fibroblast receiving sufficient levels of oxygen and nutrients supplied by the blood vessels. Healthy granulation tissue is granular and uneven in texture; it does not bleed easily and is pink / red in colour. The colour and condition of the granulation tissue is often an indicator of how the wound is healing. Dark granulation tissue can be indicative of poor perfusion, ischemia and / or infection. Epithelial cells finally resurface the wound, a process known as ‘epithelialization’. 3.Maturation phase
Maturation is the final phase and occurs once the wound has closed. This phase involves remodeling of collagen from type III to type I. Cellular activity reduces and the number of blood vessels in the wounded area regress and decrease.