A G E N C Y
Meaning of Agency: Agency is relation between an agent his principal created by an agreement. Section 182 of the Contract Act defines an Agent as ‘‘A person employed to do any act for another, or to represent another in dealings with third persons. The person for whom such act is done, or whom is so represented is called the principal”.
Essential Features of Agency
- The principal
- The agent
- An agreement
- Consideration not necessary
- Representative capacity
- Good faith
- The competence of the principal
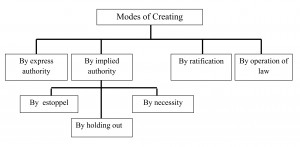
Modes or Methods or Creation of Agency
1. Agency by express agreement[Section 186 and 187]
A contract of agency may be made by express words, whether written or oral.
2. Agency by implied agreement[Section 187]
‘‘An authority is said to be implied when it is to be inferred from the circumstances of the case.
(a) Agency by estoppels : When a principal by his conduct or act cause a third person to believe that a certain person is his authorized agent the agency is aid to be an agency by estoppels.
(b) Agency by necessity : It mean the agency which comes into existence when certain circumstances compel a person to act as an agent for an other without his express authority.
(c) Agency by holding out : When a principal by his active conduct or act and without any objection permits another to act as his agent, the agency is the result of principal’s conduct as to the agent.
3. Agency by ratification [Section 196]
Ratification means confirmation of an act which has already been done. Sometimes, an act is done by a person on behalf of another person but without another person’s knowledge and authority. If he accepts and confirm the act, he is said to have ratified it.
4. Agency by operation of law:
In certain circumstances the law treats a person as an agent of another person.
For example, (a) when a partnership is formed, every partner automatically becomes agent o another partner. (b) when a company is formed its promoters are treated as its agents by operation of law
RIGHTS AND DUTIES OF AGENT
Rights of an Agent
- Right to retain money received on principal’s account.
- Right to receive remuneration.
- Right of lien on principal’s property.
- Right to be indemnified.
- Right to compensation for injury caused by principal’s neglet.
Duties of an Agent
- To follow the direction of the principal.
- To conduct the business of agency with reasonable skill and diligence.
- To render accounts on demand
- To communicate with the principal.
- Not to deal on his own account
- To pay the amounts received for the principal
- Not to delegate his authority
- Not to act in excess of authority
- Duty on termination of agency by principal’s death or insanity.
TERMINATION OF AGENCY
Termination of agency means revocation (cancellation) of authority of the agent the modes of termination of agency may be classified are as :
(a) Termination of Agency by the act of the Parties.
- By revocation o authority by the principal
- By renunciation (giving up) of business of agency by the agency
- By mutual agreement
(b) Termination of agency by Operation of Law
- Completion of business of agency
- Death or insanity of principal or agent
- Insolvency of the principal
- Destruction of subject matcer
- Expiry of time
- Agency subsequently becoming unlawful.
- Termination of sub agent’s authority


Nice notes
Amazing notes, covering almost all points of the topics.
Some points may be further added:-
DEFINITION OF INDEMNITY AS PER ENGLISH LAW
INDEMNITY AND INSURANCE
CLAIM OF LOSS BEFORE PAYMENT
– Usman Jamal vs. Gopal Purushottam, 1928 ILR, Kolkata
METHOD OF CREATING INDEMNITY OBLIGATIONS
SITUATIONS OF TYPES OF INDEMNITY CREATION
LIABILITY OF INDEMNIFIER
COMMENCEMENT OF LIABILITY OF INDEMNIFIER
DOCUMENTS AGREEMENTS OF INDEMNITY
LIABILITY OF SURETY
RIGHTS OF SURETY
POSITION OF MINOR
LETTER OF CREDIT OR BANK GUARANTEE
SURETY AS FAVOURED DEBTOR
Brikmyr vs. Darnell
CONTINUING GUARANTEE – Durga Priya Choudhary vs. Durga Pada
EXTENT OF SURETY’S LIABILITY S.128
FINDER OF GOODS AS BAILEE
ACTUAL DELIVERY AND CONSTRUCTIVE DELIVERY (Fazal vs. Salamat Rai)
RIGHT TO DISPOSE OF THE GOODS
BAILMENT AND HIRE PURCHASE
PLEDGE BY CERTAIN SPECIFIED PERSONS MENTIONED IN THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT
KINDS OF AGENTS AND AGENCIES
DISTINGUISHEMENT BETWEEN AGENT AND SERVANT
LIABILITY OF PRINCIPAL FOR AGENT’S MISCONDUCT AND TORT
LIABILITY OF PRINCIPAL AND AGENT BEFORE AND AFTER TERMINATION
*Over all the notes are superb…….!!!
hi
I really appreciate you taking the time to comment…Suggestions and new ideas are always welcome. I’ll try to add these points to this topic.
Thanks for being optimist 🙂
This is so amazing notes helps to know the whole objects ina topic good work??✋?
Thanks 🙂
Thanks… nice notes…
Really it is very useful….Tq so much?
It is in point of fact a great and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you so much this is a best not it’s helpful for my exam
I gotta favorite this website it seems handy extremely helpful
Keep up the good work! Thanks.
I truly wanted to write a brief note so as to say thanks to you for the stunning secrets you are sharing here. My extensive internet investigation has at the end of the day been paid with pleasant suggestions to share with my friends and family. I would repeat that we readers actually are unequivocally blessed to live in a very good network with many brilliant individuals with very helpful techniques. I feel somewhat grateful to have encountered your entire webpages and look forward to some more pleasurable minutes reading here. Thank you once more for everything.
Appreciate it for this grand post, I am glad I observed this site on yahoo.