Types of Plant Layout
Plant layout may be defined as a technique of locating machines, processes and plant services within the factory so as to achieve the right quantity and quality of output at the lowest possible cost of manufacturing. The layout of a manufacturing system can be classified into following categories:
1. Process Layout/Functional Layout
In this layout more emphasis is given to specialization or functional homogeneity on various components of the system. All operations of similar nature are grouped together in the same department or part of the factory. Here machines performing same type of operations are installed at one place i.e. plant is grouped according to functions e.g. drilling machines are located at one place known as drilling section. Similarly operations are classified in different sections like milling, moulding, packaging etc. This type of layout is most appropriate for job and batch type of manufacturing systems where small quantities of a large range of products are to manufactured e.g. machine tools, custom-made furniture etc.
Advantages
i. General purpose equipment is used.
ii. Changeover is rapid.
iii. Material-handling equipment is flexible.
iv. Eliminate duplication of machines.
v. Set up and maintenance costs are low.
vi. Flexibility is more (than line layout).
vii. Machines breakdown does not disrupt production schedule.
viii. Lower capital investment.
ix. Supervision can be more effective and specialized.
x. There is a greater scope for expansion.
xi. Each production unit works independently.
Disadvantages
i. Longer processing time.
ii. Requires more floor space.
iii. Inspection is more frequent and costlier.
iv. More material handling due to backtracking of material.
v. More skilled labour is required resulting in high-labour costs.
vi. Technical supervision is required.
vii. Work-in-progress inventory is high requiring greater a storage space.
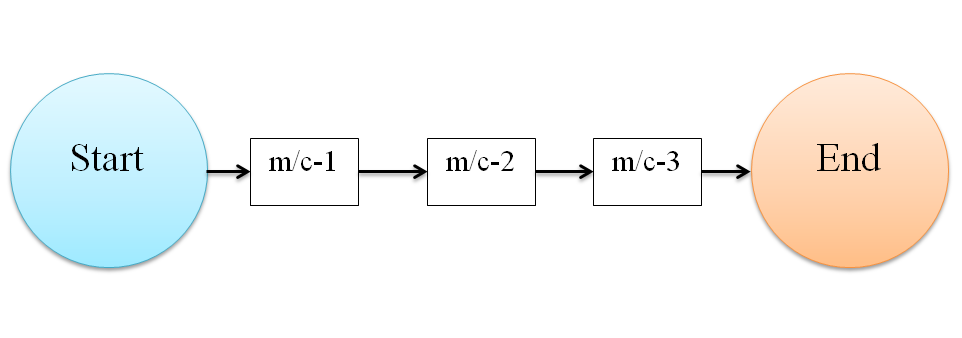
2. Line or Product Layout
This layout is designed as per the sequence involved in manufacturing process as shown in the following figure. It is assumed that materials are transformed into products through a series of integrated operations ( the order of the operations cannot be changed) arranged in a ordered sequence. The position and order in the sequence for a machine performing particular operation is fixed. Once a machine is in line, it cannot perform any operation, which is not designated in the sequence of operations. The material moves from one workstation to another sequentially without any deviation. The raw materials are fed at one end ad taken out as the finished product on the other.
In general there are five types of product layout:
a) Paced line layout
In this type of line layout, the workstations are connected through a conveyor belt which moves at fixed speed. Workstation stoppage time is fixed. The workmen have to perform their task in that stipulated time only. There is continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials. Conveyor belt is a life line of this layout. Some of the characteristics of a placed line layout are:
- Cycle time is decided by speed of conveyor. Workstations are connected through a conveyor belt.
- Conveyor moves at fixed speed. Workstations are properly balanced in respect to job to perform at every station.
- There is continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials.
b) Unpaced line layout
In this type of lie layout, the workstations are connected. There is continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials. Job speed at each work station is different. Some of the characteristics of unpaced line layout are:
- Each workstation is a separated entity but connected in sequence.
- Each workstation processes unit at its own rate.
- Cycle time is decided by performance of the slowest machine. Material handling equipment is independent of another.
- Workmen requirement is different for each workstation.
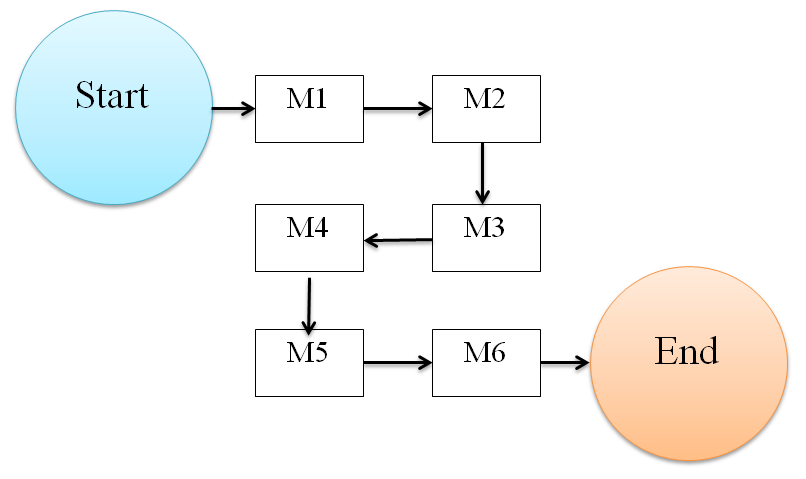
c) Serpentine layout (Zig-Zag)
In this type of line layout, the workstations are connected in zigzag manner as shown in the figure. There is a continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials. Job speed at each workstation is different but in a sequence some of the characteristics of serpentine linelayout are:
- Workstations are connected in zigzag manner.
- Each workstation is connected in sequence.
- Each workstation processes unit at its own rate. Material-handling equipment is independent of another.
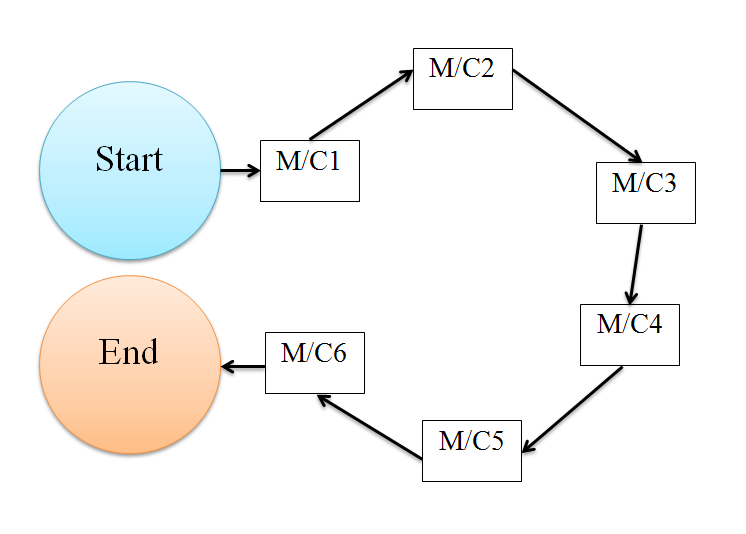
d) Circular layout
In this type of line layout, the workstations are connected in circular or semi-circular manner as shown in the figure. There is a continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials. The job speed at each workstation is different, but in a sequence. The workstations are connected in circular or semi-circular manner. Some of the characteristics of circular lien layout are:
- Each workstation is connected in a sequence.
- Each workstation processes unit at its own rate.
- Material handling equipment is independent of another.
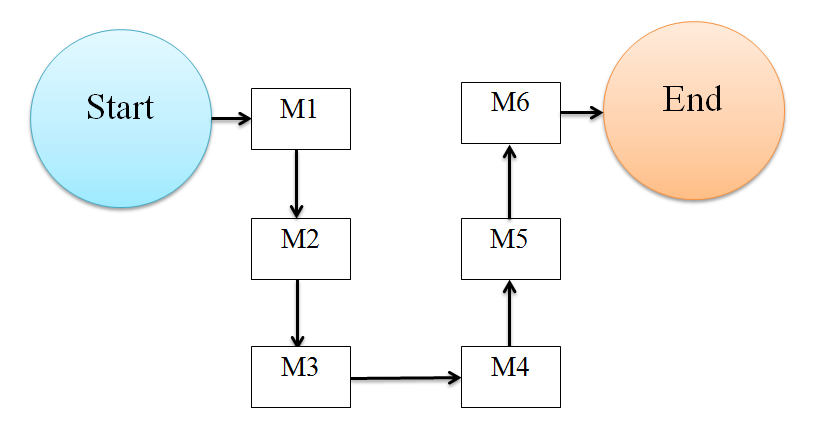
e) U-shaped layout
In this type of line layout, the workstations are connected in a U-shaped manner as shown in the figure. There is a continuous and uninterrupted flow of operations and materials. The job speed at each workstation is different, but in a sequence. Some of the characteristics of a U-shaped layout are:
- The workstations are connected in circular or semi-circular manner.
- Each workstation is connected in sequence.
- Each work station processes unit a its own rate. Material handling equipment is independent of another
Advantages
i. Since the distance to be travelled by material is small, material handling costs are less.
ii. Ensures smooth and regular flow of materials and finished goods.
iii. Less inspection is needed because of routine operations.
iv. Production control is simple as the line integrates different production stages and allows least number of planning and control operations.
v. Low cost labour procurement and lesser training requirement.
vi. Optimum use of floor space and less congestion of work in the progress.
vii. Low cost of manufacturing per unit.
viii. Semi-skilled workmen can also be accommodated in the manufacturing operations.
Disadvantages
i. Project cost increases because of duplication of machines.
ii. More receptive equipments are required.
iii. Breakdown of one single machine disturbs whole line.
iv. Individual incentive scheme is not possible. Less flexibility of operations.
v. Heavy overload charges due to underutilization of machines.